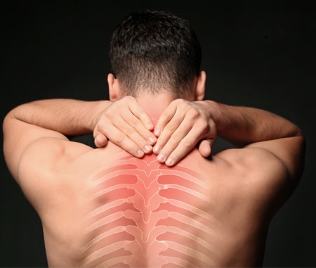
The disease osteoarthritis is the most common disease of all diseases of the spine. Such as osteochondrosis, right is a burned-degenerative lesion of the drive are located between the vertebrae, then as a consequence this leads to a permanent change in the structure, as well as the shape of the hard drives.
With increasing age of the people, the changes in his spine are developing more and more, and age over 40 to 45 years of osteochondrosis all suffering almost. Self-osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine develops much less frequently than, for example, lumbar or cervical parts of the spine, because the vertebrae in him much less mobile than other vertebrates areas. In addition, the area in the area of the back of the Thorax is a more developed corset of muscles that support the spine in the area of the thoracic spine is much better than in others.
What is the Thoracic osteochondrosis is?
Thoracic osteochondrosis directly is a layering of the discs between the vertebrae, while reducing its thickness and, as a consequence, followed by a pinched nerve in the intercostal space of the thorax of the Person.
However, we will note once again that due to the fact that a physiological Fixation of the ribs in man, rather stiff, the part of the spine in the thoracic region, the least susceptible to the disease osteochondrosis.
In General, in this process, the pathology of the discs between the vertebrae in the chest Department, the twelve thoracic vertebrae are involved. But the most common in the case of the osteochondrosis of the thoracic pathological changes occur in Wernigerode the vertebrae. There are different degrees of lesion in breast osteochondrosis, and then we will consider them in more detail.
Predisposing factors to the development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The exact causes of the emergence of osteochondrosis thoracic spine of modern science until the end not yet installed. At the Moment, it is common in medicine, the following predisposing factors, or so-called risk factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessive physical stress;
- Injuries of the spine, such as, for example, a fall or injury;
- changes with age in the intervertebral discs and lead to a reduction in hydration in the tissues of the drives;
- Circulatory disorders in the area of the chest.
Causes of the disease, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
In the main degree of the development of the disease osteochondrosis, in General, promotes physical inactivity, that is, the noticeable lack of muscle-strains, leading to a weakening of the functions of the muscular corset and, as a consequence, to an increase in the loads on the intervertebral discs and the ligaments.
Other, additional reasons for the development of the thoracic degenerative disc disease are:
- Under cooling;
- the presence of chronic stress situations;
- the transmitted infections;
- in severe conditions, and physical work;
- caused hormonal disturbances in the body;
- Violation of metabolism in the body;
- the presence of deformities of the spine.
In the Wake of the impact of the combination of these factors, or sometimes even a, in the discs between the vertebrae, over time, develop burnt-irreversible degenerative processes:
- purposee core of the intervertebral disc gradually begins to lose fluid, the position of the lubricant's ability to function, which ultimately reduces considerably, depreciation and amortization, the function of this drive was allocated to;
- more fibrous ring of the vertebrae themselves, in view of the increasing pressures on him more vulnerable, which, in turn, leads to their progressive destruction.
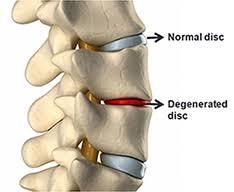
Symptoms of breast osteochondrosis and its symptoms
Clinical symptoms of thoracic spine degenerative disc disease are completely dependent on these factors:
- The age of the patient;
- the severity of the disease;
- Stage of osteochondrosis thoracic spine: Remission or exacerbation.
The main features of the intervertebral disc degeneration, thoracic are:
- Pain in the chest in the area of the spine, the so-called - Dorigo;
- painful damage to the nerve endings of the spinal cord – radiculopathy;
- Abdominal Syndrome;
- cardiac syndrome or changes in the heart muscle, with the characteristic pain, which is also under the influence of nitroglycerin;
- pulmonary syndrome, to nip in the Form of congestion of the lungs with signs of hypoxia, that is.
The increase in the temperature of the body of the patient in the case of the osteochondrosis observed that a direct differential diagnostic function. Dorsalgia in the chest area shows the occurrence of cracks in the fibrous Ring, and deformation of the nucleus pulposus. In the implementation of the to feel, this pain the chest area only reinforced.
In addition, typical symptoms of a chest of drawers osteochondrosis asked myelopathy, i.e., deformation of nerve endings, are:
- the feeling of "goose bumps" - paresthesia;
- Pain along this way nerve;
- Reduction of the sensitivity to temperature and touch;
- Violation of the motor function in the spine.
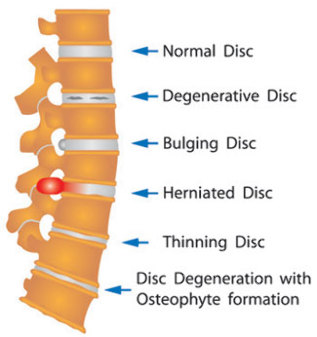
The extent of the disease breast osteochondrosis
Different degrees of the disease breast osteochondrosis by each of its pathology, each of which has only its own clinical symptoms. Of modern medicine, there are four degrees of osteochondrosis of the thoracic and, accordingly, four periods of their development. We consider them in more detail.
The first degree, for which it is characteristic that within the fibrous ring cracks occur in the later penetrates purposee core. This period of the development of the disease breast osteochondrosis characterized by the following features:
- Emergence of pain in the spine at the site of the lesion, but not completely outside of the localization of the occurrence of the disease;
- the pain can wear, like durable in nature and are in the Form of lumbago;
- spasm occur-like contraction of the muscles, accompanied by pain in the inner area.
The second stage, as a period of development of the breast osteochondrosis, due to an abnormal emergence of an increased mobility with the following clinical symptoms:
- appear subluxations of the spine in the chest;
- the pain during the journey;
- there are complaints in the case of long pose continued.
The third degree, characterized by a period, if the fiber ring is torn and its limits purposee core. In this Phase of the disease, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine bulbosus hernia appear, the clinical symptoms are pretty hard. Namely, Neuro-vascular, muscular-tonic and Reflex-degenerative.
In addition to the given, the third degree of intervertebral disc degeneration, thoracic, a characteristic change of the States of the spine is:
- weak fixation of the provisions of the spine;
- Restriction of the mobility of the spine Department, is manifested in the Form of kyphosis or scoliosis.
The fourth stage, connected with this period, in the case of the burnt-degenerative process affects all structures in the vicinity of the spine. In this pathological yellow, inter-spinal and other ligaments, and in the structures around the spine, involved a fibrosis is formed. In this period of the disease breast osteochondrosis, clinically, the so-called, the state of Remission observed.
Complications are possible in the case of osteochondrosis
With further progression of the disease breast osteochondrosis progresses, the development of accompanying complications, such as, for example:
- Inflammation of the nerve endings of the spinal cord;
- The Band's performance hernias;
- the development of vascular dystonia;
- the development of the fracture Schmorl ' s;
- Disease spondylosis;
- the pathological Proliferation of the bony growths - osteophytes;
- a significant reduction of the vertebral canal.
It should be noted that the severity of the complications that can arise in the case of osteochondrosis is completely dependent on the pace of progress of the process occurring disease, and, of course, the efficiency of the treatments for degenerative disc disease of the thoracic spine.

Diagnosis of breast osteochondrosis and their methods
In practice, a number of methods for the diagnosis of breast osteochondrosis. The most common of them is an x-ray examination, whose results are rather informative. Signs of breast osteochondrosis, identify in this study are:
- hurt the contours of the discs between the vertebrae;
- the edges of the plates of epithelial cells in the shaft have acquired-shaped character;
- the intervertebral disc changes its shape;
- the resulting osteophytes – bony pathological growths;
- enlarged and sharpened uncinate processes of the vertebral body;
- the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae changes its normal shape;
- clearly, the size of the height of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae is reduced;
- the resulting herniated discs between the vertebrae.
In some cases, the method for the diagnosis of breast osteochondrosis by means of x-ray density study defined the following signs of this disease:
- in the case of the started pathology contrast medium, the disc fills in between the vertebrae completely;
- with the help of contrast medium visible in the contours of the nucleus pulposus, the unequal are;
- in the case of the destruction of the intervertebral disc is largely a contrast agent penetrates beyond it, to penetrate into the spinal canal.
The treatment of the osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The implementation of the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis may be applied to one of the following methods, taking into account the results of the thoracic diagnosis of osteochondrosis, namely:
- conservative-traditional treatment;
- Treatment of thoracic degenerative disc disease with the help of routes;
- surgical Intervention.
Nothing new, of course, is not invented yet, and as such, treatment of the thoracic spine degenerative disc disease, the so-called conservative, is already diseases a Tradition for the treatment of any type of degenerative disc. In any case, always preferred conservative-medical method for the treatment of thoracic intervertebral disc degeneration by the appointment of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the relief of pain. It is important to note that these drugs roots very well inflammation and resulting swelling, to eliminate a contribution to the reduction of the process of compression of the nerve. In more complex cases, thoracic osteochondrosis, the treating physician a number of drugs, for example, some strong painkillers and muscle relaxants, which prevent the emergence of muscle spasms may prescribe in addition.
If the pain disappears, or she was able to be cut, i.e., during a Remission, is in addition to the treatment of physiotherapy, but also, besides that, movement therapy and Massage. The main means of struggle, and the prevention of this disease in the treatment of physical therapy, magnetic field therapy by means of special medical devices.
Apart from the above, for the treatment of breast, arthritis can very successfully be used for traction treatment, i.e. the treatment of the thoracic spine degenerative disc disease by a special traction. In this method, paravertebral muscles, tissue and ligaments stretching are exposed, that the Band leads to an increase of the distance. Even one and a half mm is enough to reduce swelling, the elimination of constriction, but also tension in the surrounding muscles of the spine.
And here surgical intervention is advisable only if the above-mentioned methods of treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is not the desired result.